USD/INR weakens ahead of Fed’s Goolsbee speech
- The Indian Rupee gains traction in Monday’s early European session.
- Significant foreign outflows and Trump trades might drag the INR lower.
- The Fed’s Goolsbee is set to speak later on Monday.
The Indian Rupee (INR) gathers strength on Monday amid the modest decline in the US Dollar (USD). However, the renewed Greenback demand from investors and weakening of the Chinese Yuan are likely to keep pressure on the Iocal currency in the near term. Additionally, the unabated foreign fund outflows contribute to the INR's downside.
The routine intervention by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) by selling USD might help limit the Indian Rupee’s losses, though this has led to a drop in India's forex reserves. In the absence of top-tier Indian and US economic data releases due on Monday, the focus will remain on risk sentiment and the speech from US Federal Reserve (Fed) Austan Goolsbee.
Indian Rupee recovers, but potential upside seems limited
- The Indian Rupee is expected to be trading at 84.5 per US Dollar by the end of December this year, according to the median forecast of the Business Standard poll.
- Moody's Ratings estimated the Indian economy to grow by 7.2% in 2024, driven by a gradual recovery in household spending and easing inflation pressures. The rating agency further projected growth rates of 6.6% and 6.5% in 2025 and 2026.
- "We remain negative on the outlook for Asian FX through H1 2025, given the potential negative economic impact of likely US tariff hikes," MUFG Bank said in a note.
- The US Retail Sales rose 0.4% in October, compared to 0.8% recorded in September (revised from 0.4%), the Commerce Department's Census Bureau revealed on Friday. This figure was stronger than the 0.3% expected.
- Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee said on Friday that markets tend to overreact to interest rate changes and that the Fed should maintain a slow and steady approach to reaching the neutral rate.
- Boston Fed President Susan Collins noted that another rate cut in December is on the table, but it is not a "done deal," per Reuters.
- The markets have priced in nearly 60% of the 25 basis points (bps) rate cut by the Fed at the December meeting, according to the CME FedWatch Tool.
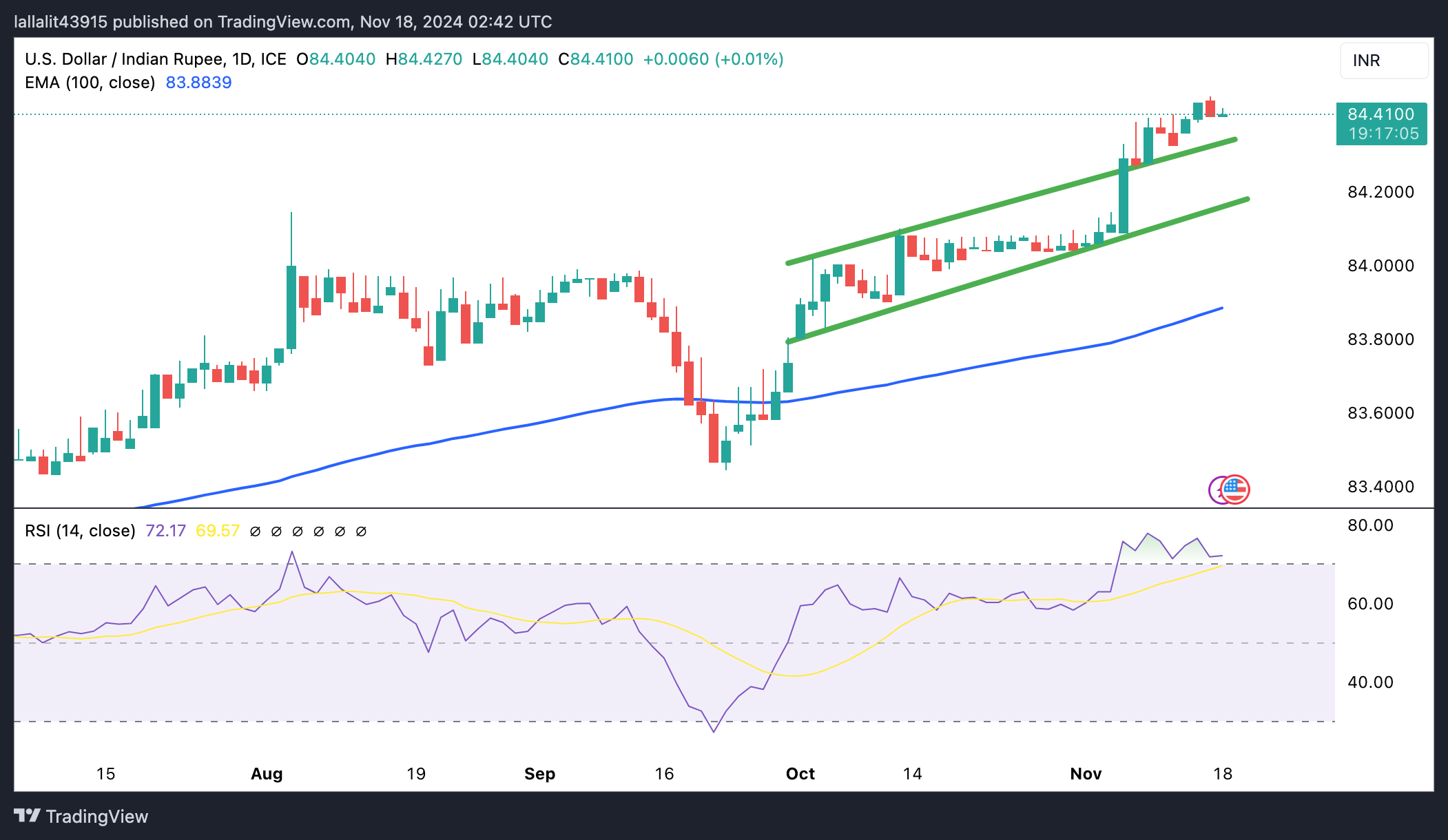
USD/INR still maintains its positive bias in the longer term
The Indian Rupee trades firmer on the day. The longer-term uptrend of the USD/INR pair remains intact as the pair holds above the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) on the daily chart. Nonetheless, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) exceeds 70, indicating an overbought condition. This suggests that additional consolidation cannot be ruled out before positioning for any near-term USD/INR appreciation.
The resistance level to watch if buyers step in would be 84.50. A break above this barrier could pave the way for a test of the 85.00 psychological level.
On the other hand, the resistance-turned-support level at 84.35 acts as an initial support level for the pair. If the support level fails to hold, bears could push prices lower toward 84.00, the round mark. The additional downside threshold is seen at 83.88, the 100-day EMA.
Indian economy FAQs
The Indian economy has averaged a growth rate of 6.13% between 2006 and 2023, which makes it one of the fastest growing in the world. India’s high growth has attracted a lot of foreign investment. This includes Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into physical projects and Foreign Indirect Investment (FII) by foreign funds into Indian financial markets. The greater the level of investment, the higher the demand for the Rupee (INR). Fluctuations in Dollar-demand from Indian importers also impact INR.
India has to import a great deal of its Oil and gasoline so the price of Oil can have a direct impact on the Rupee. Oil is mostly traded in US Dollars (USD) on international markets so if the price of Oil rises, aggregate demand for USD increases and Indian importers have to sell more Rupees to meet that demand, which is depreciative for the Rupee.
Inflation has a complex effect on the Rupee. Ultimately it indicates an increase in money supply which reduces the Rupee’s overall value. Yet if it rises above the Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) 4% target, the RBI will raise interest rates to bring it down by reducing credit. Higher interest rates, especially real rates (the difference between interest rates and inflation) strengthen the Rupee. They make India a more profitable place for international investors to park their money. A fall in inflation can be supportive of the Rupee. At the same time lower interest rates can have a depreciatory effect on the Rupee.
India has run a trade deficit for most of its recent history, indicating its imports outweigh its exports. Since the majority of international trade takes place in US Dollars, there are times – due to seasonal demand or order glut – where the high volume of imports leads to significant US Dollar- demand. During these periods the Rupee can weaken as it is heavily sold to meet the demand for Dollars. When markets experience increased volatility, the demand for US Dollars can also shoot up with a similarly negative effect on the Rupee.
Forex News
Keep up with the financial markets, know what's happening and what is affecting the markets with our latest market updates. Analyze market movers, trends and build your trading strategies accordingly.
